Screens Express is a great solution to the problem of remote troubleshooting for family members, friends or clients. Simply download and run this free utility on the Mac you wish to control and connect via Screens. It's that easy! If you’ve been given permission, you can view and control the screen of another Mac on your network. On the Mac you want to share, choose Apple menu System Preferences, click Sharing, select Screen Sharing, then note the name and address of the Mac (it’s listed on the right). The name looks like “iMac (7)” or “Joe’s MacBook Pro.”. Mar 11, 2018 Step 1, Open System Preferences on the computer you plan to connect to.Step 2, Click the Sharing icon.Step 3, Check the box correlated to Remote Login. This turns on your SSH setting.
- Mac Software Controlling Multiple Macs Remotely Access
- Remote Control A Mac
- Mac Software Controlling Multiple Macs Remotely Iphone
- Mac To Mac Remote Control
- Mac Software Controlling Multiple Macs Remotely Support
Remote control of your Macintosh allows you to access a remote (host) computer across a network or the Internet from a local (client) system. The screen of the shared host computer appears locally, and you use your mouse and keyboard to control the other system from afar. Historically there have been fewer options to accomplish this for Macs than PCs, but the situation has been improving steadily.
Part 1 of this covers general considerations and Apple-supported methods available for remote system control that will generally work on any version of Mac OS X (Jaguar, Panther, Tiger, and Leopard). Part 2 addresses some commercial solutions that also support multiple OS versions, along with how to force-reboot a remote Mac. Part 3 looks at on new options provided by Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard.
General Considerations
Remote control capabilities vary by method used and include remote desktop control (screen sharing), file transfers, and system management (patches and updates). With any remote desktop method, access to the remote system is slower than when you are sitting in front of that computer. The method used, network bandwidth available, and types of traffic will determine the “sluggishness” factor.
Minimizing the amount of data you need to transmit for screen sharing will make the process run more quickly. Closing unnecessary windows on the remote system and using a flat single-color desktop (instead of a complicated picture or pattern) will speed up response. Patience is a must, but remember it’s usually faster than traveling there!
Mac Software Controlling Multiple Macs Remotely Access
Needs and realities often dictate your options. Some remote control methods work across different versions of the Mac OS (or cross-platform), while others require the same OS version on local and remote machines. Some methods require you to know the IP address of the remote system to connect and may require special firewall configurations, while others will work without any special settings or knowledge – usually!
It’s often helpful to use two remote control methods simultaneously (if possible), especially if you’re running a server or access is otherwise critical. Programs crash, network and Internet conditions vary, and you may find yourself locked out at a critical time. Sometimes method B works when method A doesn’t; then you can fix method A or reboot the machine from afar.
Apple Remote Desktop (ARD)
Apple’s native remote control solution is Apple Remote Desktop (ARD). ARD server software has been built into Mac OS X since 10.3 Panther and was available as an optional install for earlier versions of OS X. ARD provides the full gamut of remote system control: scalable screen sharing, file transfers to and from the remote systems, and remote software updating of individual machines and whole networks at a time. On a LAN, network admins with multiple Macs to manage will find this tool indispensable.
To enable an ARD host (server) in Panther and Tiger, go to System Preferences –> Sharing and turn on Apple Remote Desktop, then click Access Privileges and enable all desired services for one or more users. In Leopard you also enable ARD via System Preferences –> Sharing, but control capabilities have been split into separate Screen Sharing and Remote Management sections; click Options for choosing Remote Management services. ARD access from afar is via your host Mac’s account password.
To control an ARD-shared host computer, you need to use the Apple Remote Desktop administrator software. Apple sells two versions, a 10-client version for $299 or an unlimited client version for $499. The client limit dictates how many remote systems you can manage simultaneously; most home users and small business will be fine with the 10-client version. Bonjour support is available to find systems on your local network, or you can add them by IP address.
Across the Internet you must know the IP address of the remote computer or network gateway to establish a connection; this requires either a static IP address on the remote end or the use of a dynamic DNS locator service (like DynDNS) to find your remote system in times of need. ARD requires forwarding TCP and UDP ports 3283 through firewalls. Traffic can be routed across VPNs if one is available.
ARD is a powerful tool, but power comes at a price. Fortunately for home and small business users there are other options.
Virtual Network Computing (VNC)
VNC is an open source software effort to provide cross-platform remote screen sharing capabilities. Long an option for Windows, VNC support was spotty on Mac OS 9 but is solid on Mac OS X. It has become my primary method of controlling remote Macs and PCs from other Macs (and PCs) when static IP addresses are available.
The remote Mac needs to run a VNC server; starting with Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger the built-in ARD software has included the option to use VNC for screen sharing. Go back to System Preferences –> Sharing –> Apple Remote Desktop (Tiger) or Screen Sharing (Leopard) and click the Access Privileges or Options button (as applicable). Enable Share Screen with VNC clients and use a strong password.

On pre-Tiger Macs or as an alternate option for all Macs, the free Vine VNC Server (for OS X and OS 9) and it’s older precursor, OSXvnc, offer excellent VNC server packages with more options than Apple’s built-in server. In my experience the Vine and OSXvnc packages are more stable and resilient than Apple’s built-in server – I’ve had onboard VNC stop working many times and require a reboot to fix, while the standalone server rarely fails. I use Vine VNC Server on many of the business systems I support.
A VNC client viewer application is required to view your remote Mac on your local system. Apple did not provide a VNC viewer in Mac OS X until 10.5 Leopard (see Part 3 of this series), but the open source market came earlier to the rescue. Chicken of the VNC is a good free VNC viewer with a silly name, and it runs on Mac OS X 10.3 Panther through 10.5 Leopard.
For a step up, $30 will get you the Vine VNC Viewer; this software is faster and more stable than Chicken of the VNC, and it offers screen size scaling (invaluable when controlling a big screen from a small laptop) and clipboard sharing. Mac OS X Tiger or Leopard is required.
Both Vine and Chicken of the VNC will find local network systems using Bonjour. Across the Internet you will need to know the IP address of the remote computer or use a dynamic DNS locator service. VNC uses TCP port 5900 for control and, as with ARD, requires port forwarding through firewalls and routers. VNC works fine across VPNs.
VNC provides screen sharing capabilities without file transfers. To work around this limitation you can use a network and/or Internet-accessible resource that both systems can reach: an FTP server, a shared Mac disk using AFP (AppleShare), a shared Windows volume using SMB, or a webserver with upload/download capability. Post the software or document from one system and grab it from the other via your shared disk or server.
Continued in Software to Remotely Control and Reboot Your Mac.
Methods of Mac Remote Control
- Part 1: Remotely Control Your OS 9 or OS X Mac
This article was originally published on Adam’s Oakbog website. It has been adapted and reprinted here with his permission.
Keywords:#appleremotedesktop #vnc
Short link: http://goo.gl/DZUs4C
searchword: macremotecontrol
Remote access to Mac, anywhere
While many countries are on a lockdown due to COVID-19, remote work is becoming a lifestyle. Remotely accessing a Mac is designed to be easy. Apple has spent a lot of time ensuring anyone can log in to their Macs — both desktop and laptop — from any other Mac device, anywhere. And, besides, there are a variety of third-party apps ready to help with that too.
Still, remotely managing their Mac sounds overly complicated to a lot of people. From how you connect to sharing files or screens to using your Apple device as a remote mouse, we want to demystify the process in the easy-to-follow guide below.
Best Remote Access Apps for Mac
There are times when you want to access your Mac remotely, and there are many different solutions to remote access your Mac. Best utilities in one pack, give it a go!
How to access your Mac from another location
There're two ways: you can allow remote login to your Mac from another computer, or allow others to access your computer using Remote Desktop (it's available from the App Store).
Allow remote login to your Mac from another computer
For devices using the same macOS, you can allow remote Mac login using a Secure Shell (SSH). This enables Mac remote desktop access using a Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
To set up Remote Login:
- Go to System Preferences > Sharing
- Select Remote Login.
- Choose which users you want to have remote access or the ability to control your Mac.
Remote Control A Mac
You can either select All Users, which means any other device on your network, or any Mac you own, can access and connect, or click the plus sign to pick the exact users.
Mac Software Controlling Multiple Macs Remotely Iphone
When you want to remotely log in to your Mac from another device, you need to know your username (the name that appears when you login) and your computer's IP address. Write them down and keep them safe, as allowing access to your Mac does make it potentially less secure, especially over cellular or public Wi-Fi networks.
Mac To Mac Remote Control
Accessing, controlling, or viewing information on your Mac can be done with a built-in Terminal or any other SSH app using your username and IP address.
Mac Software Controlling Multiple Macs Remotely Support
Allow others to access your computer using Apple Remote Desktop
With macOS Sierra remote Mac access and control is even easier. To set up it:
- Go to Menu > System Preferences > Sharing
- Select Remote Management - it should appear as a checkbox.
- Now you can select who has remote desktop access. Either select, All Users, which means any other device on your network, or Mac you own, can access and connect, or click the Add button(+), which gives you the ability to select who can have remote access and/or control.
If you are using a VPN or VNC viewer and want to access your Mac remotely, you will need to setup a password first. It is also possible to use iOS devices, such as an iPhone and iPad, through Apple Remote Desktop, available from the App Store.
How to stay on the same page with Screens
Collaboration has become of utmost importance to today's workplaces. And with more and more people working remotely, being on the same screen (ahem, page) is a must.
Screens allows you to work remotely with any computer regardless of your location. Whether you are on a business trip or traveling, stay confident knowing you can access any file on your home computer at any time.
This robust screen sharing tool for Mac supports:
- Multiple displays
- Drag-and-drop file sharing
- Hiding your remote screen while accessing it
- Accessing other computers (e.g. colleague's) as a guest
- Alternative shortcuts (useful when connecting Mac to PC)
- Custom actions in case of disconnection
To start using Screens, get the app from Setapp and configure the following:
- Remote login and remote management (as per the guide above)
- Install Screens Connect helper app and create a Screens ID on every machine you'd like to connect to in the future
- Use your Screens ID in the Screens app and it will automatically determine which of your computers are available for connection
Remote desktop client for Mac
Control any computer remotely – a perfect way to access your Mac from anywhere without limitations.
Share files between devices
Today we have plenty of ways to send and share files. But ask someone to send something, and you are likely to get it through email. Due to the ubiquitousness of email, it's still the default method for file sharing, despite its obvious flaws and constraints.
Fortunately, there are much better ways:
Native macOS File Sharing
Few people know that their Mac has native file sharing functionality built in. To use this feature, activate it in the Sharing pane of System Preferences by checking File Sharing. If you only want to share specific folders, add them to the Shared Folders list. If you only want specific users to access the folder, add them to its Users list. Otherwise, everyone will be able to access it.
AirDrop
Although not the most reliable solution, AirDrop works fine for occasional sharing a file between Apple devices. In the Finder, choose Go and then AirDrop on both the sending and receiving Mac. As soon as you see the receiver's user icon, drag the desired file onto it to send.
Read more about how to use AirDrop
Dropshare
If you don't want to send files Mac-to-Mac directly but rather through a cloud storage, there is no easier way than Dropshare. The app works with numerous cloud providers, from Dropbox to Google Drive, and saves your files for sharing by simply dragging them onto its menu bar icon.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
The most technical but also the most robust way to share files from your mac is to use FTP, which you could do either through Terminal or an FTP Client, the latter being much more user friendly.
There are a few popular FTP clients one could choose from. The robust file managing app ForkLift covers most of the FTP functionality but takes it to the next level and could be a viable replacement for the Finder altogether with its quick search, instant previews, and file comparison.
DCommander is another full-featured file transfer app for Mac that combines speed and reliability, able to handle thousands of files, schedule backups, and even automate transfers.
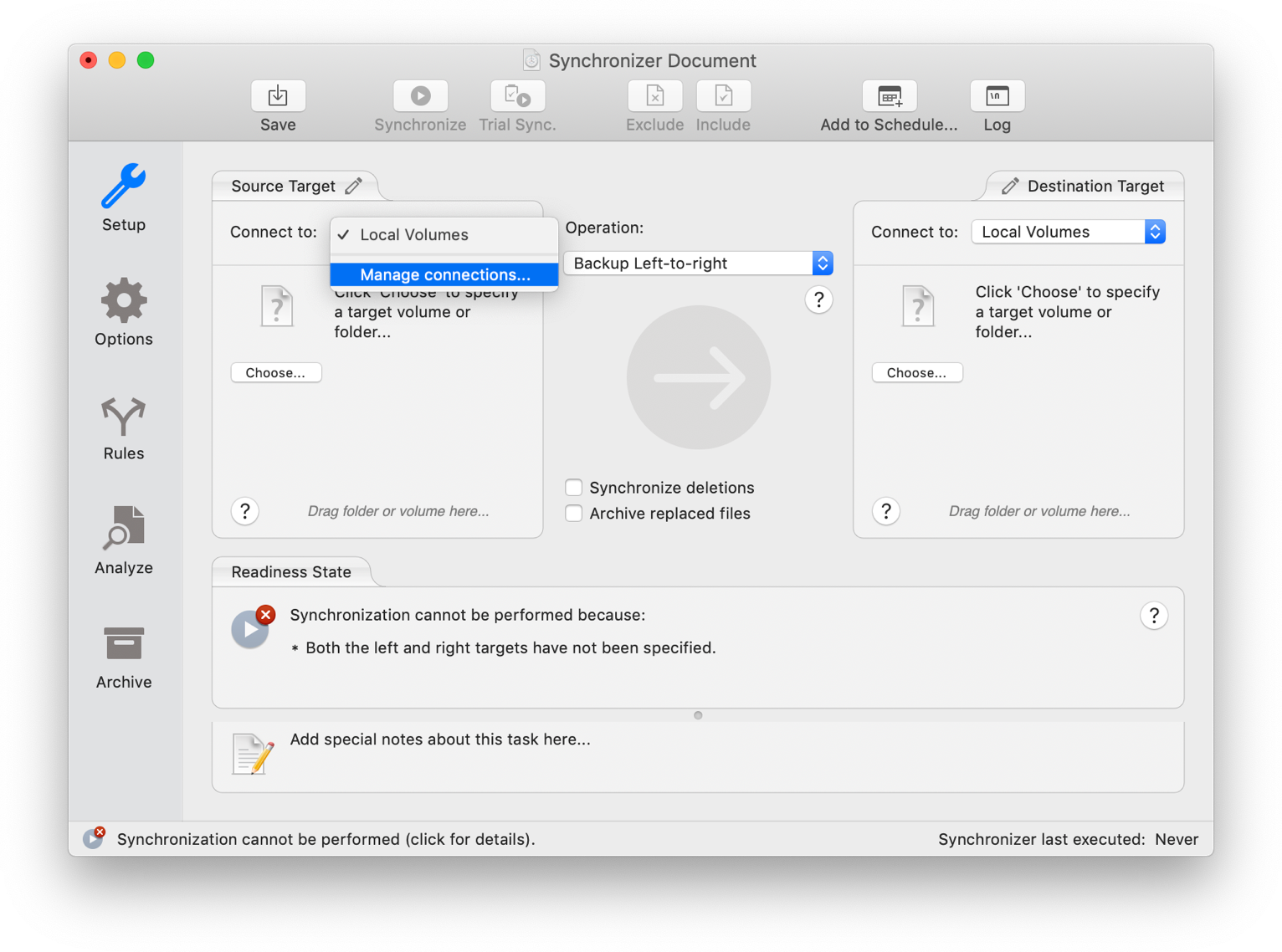
At last, when it comes to sharing the same files on different devices, an app like ChronoSync Express becomes invaluable.
ChronoSync Express is powerful tool for sharing and transferring files from Mac to Mac, or any another Apple device. With a feature called Synchronizer Document, you can select which files need to be automatically synchronized and shared between devices, just like that:
- Create a new synchronizer document for each folder synchronization you'd like to perform
- Name the synchronization
- Change the Operation to Synchronize Bidirectional
- Select folders to sync on the left and right
- Test with a Trial Sync
Do you need to use a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
Whether you are working on your Mac directly, logging into your Mac remotely, or sharing access with someone else, security should be on top of your mind.
As a rule of thumb, you should always use a VPN when connected to a public Wi-Fi network, as someone could log in and see the information you send just as easily as you do.
And with remote access — even in the View Only mode — someone can see every file and document on your Mac, except those that are password protected. Unfortunately, if you leave passwords in a visible document, you expose yourself to immense risks.
A secure VPN client for Mac like Shimo is well worth using to stop unwanted eyes from lurking around, especially if you are sharing sensitive files, financial records or customer data.
However, for extra peace of mind and security, consider firing up your VPN automatically on all networks you are not 100% sure about to keep your emails, bank accounts and personal documents safe.
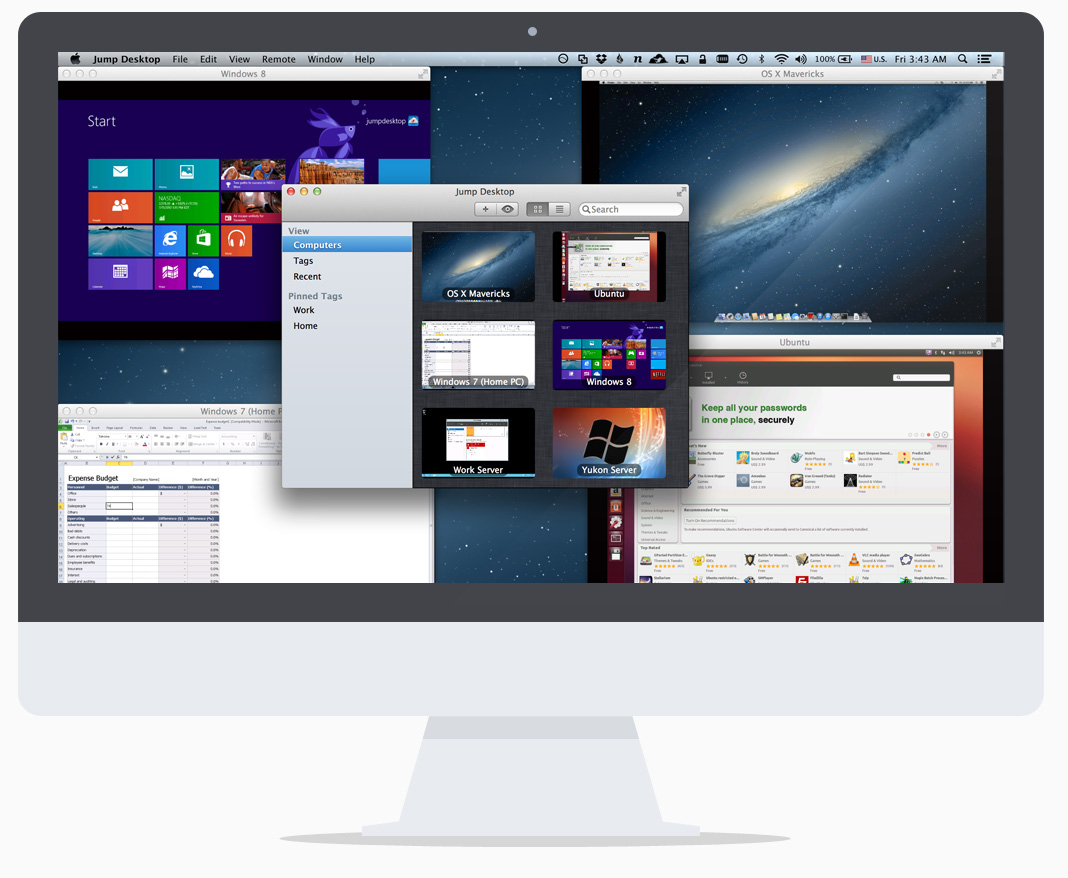
To share your Mac with someone else, download a remote Virtual Network Computing (VNC) app like Jump Desktop. With full remote access and Mac remote control, the other person — or yourself connecting to another Mac — can have the same level of control as the person using that device. Except for Admin level access, since it's password protected.
Starting with Jump Desktop is easy: either yourself (gaining access) or the person you are giving a remote view or control access to your Mac, needs to add details of the device and the password.
Secure your access with VPN
Get a VPN client for Mac to avoid privacy infringement while connecting remotely. It's secure and free to try.
Once permission is granted at the other end, remote Mac screen sharing or control (whereby you can use the iOS device as a remote mouse) becomes possible.
How to use your iOS device as a remote mouse
If your remote work starts on a patio hammock somewhere in east Asia, you should note that Apple iOS devices, such as an iPhone or iPad, can be used to control a Mac remotely, much like a mouse can control a desktop or laptop. Apps that make this possible work on VNC.
Remote Mouse is the easiest, most effective way to turn your iOS device into a wireless remote control for your Mac.
Although remote access through a local network would be most effective, since the closer you are to the device the quicker the connection, it's also possible from anywhere in the world, providing the network is secure and fast enough.
Setting up and granting access to the iOS device is the same process as when someone wants to access using a Mac. Except you need to give them a password. And make sure it is different from your primary Mac or iOS (App Store) one.
So working together or checking on your devices can be done from anywhere in the world and there are lots of ways to do that, from sharing screens and files to having complete access to a system set up far away. Setapp equips you with all the apps needed to remotely access any device you need and elevate your work to the global level.